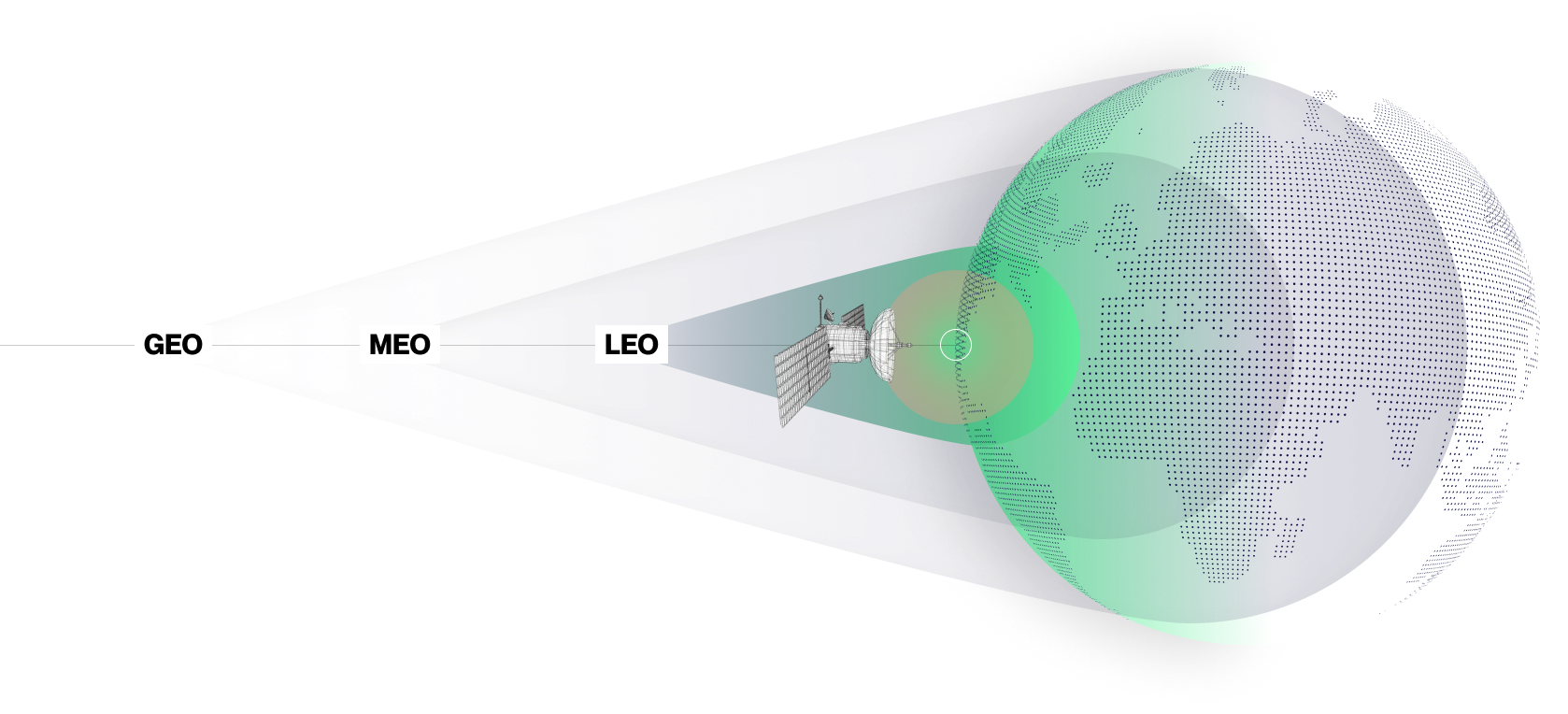
Helping to Connect a World of More than 8 Billion People
High-speed Internet (also known as broadband Internet) means access to education, healthcare, jobs, entertainment, and equal participation in the modern economy. However, broadband is only available in densely populated areas around the world. The rest of the world is still waiting. In this digitally divided world of haves and have nots, universal broadband access is the great equalizer.
With this kind of demand, it’s no wonder that the global broadband market is forecast to double within the decade. Universal high-speed Internet access for all is good for the world, and good for business.